In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of Daylight Saving Time (DST) in 2025, focusing on the early endpoint that’s catching everyone’s attention. If you’re searching for “daylight saving time 2025,” “DST end 2025,” or “time change fall 2025,” you’ve come to the right place. We’ll explore the history, impacts, global variations, and practical tips to help you navigate this annual “time travel” ritual smoothly.
As we approach the fall time change in 2025, understanding the DST endpoint is crucial for planning your schedule, health, and even business operations. The DST end in 2025 falls on Sunday, November 2, at 2:00 AM, which is notably earlier than in some previous years, prompting discussions about its implications. This article will equip you with everything you need to know about daylight saving time 2025, including why this endpoint matters and how to prepare.
For more on seasonal productivity hacks, check out our internal guide on Winter Wellness Tips or explore Time Management Strategies for Busy Professionals.

What Is Daylight Saving Time and Why Does It Exist?
Daylight Saving Time, often abbreviated as DST, is a practice where clocks are advanced by one hour during the warmer months to extend evening daylight. This “spring forward” typically occurs in March, and the “fall back” – the DST endpoint – happens in November in the United States. The concept aims to make better use of natural daylight, potentially saving energy and promoting outdoor activities.
The origins of DST trace back to ancient civilizations that adjusted daily routines to sunlight, but the modern idea was popularized by Benjamin Franklin in 1784 through a satirical essay suggesting Parisians rise earlier to save on candles. However, it wasn’t until 1895 that New Zealand entomologist George Hudson formally proposed a two-hour shift. William Willett, a British builder, championed a similar idea in 1907, leading to the first implementations during World War I for energy conservation.
In the United States, DST was first enacted in 1918 under the Standard Time Act as a wartime measure but was repealed in 1919 due to unpopularity, particularly among farmers. It resurfaced during World War II as “War Time” from 1942 to 1945. The Uniform Time Act of 1966 standardized DST nationwide, with adjustments in 1986 and 2005 extending its duration to eight months.
Globally, DST adoption varies. During the 1970s energy crisis, many European countries implemented it, and today, about 34% of countries observe DST, primarily in Europe and North America. For instance, the UK follows British Summer Time, while countries like Russia abandoned seasonal changes in 2014 for permanent standard time.
Why does DST persist? Proponents argue it reduces energy consumption by decreasing the need for artificial lighting in the evenings. However, studies show mixed results, with some indicating negligible savings or even increases due to higher air conditioning use in warmer months. Economically, industries like retail and sports benefit from extra evening daylight, boosting consumer spending.
For a deeper dive into historical timekeeping, visit our History of Clocks and Time Zones page.
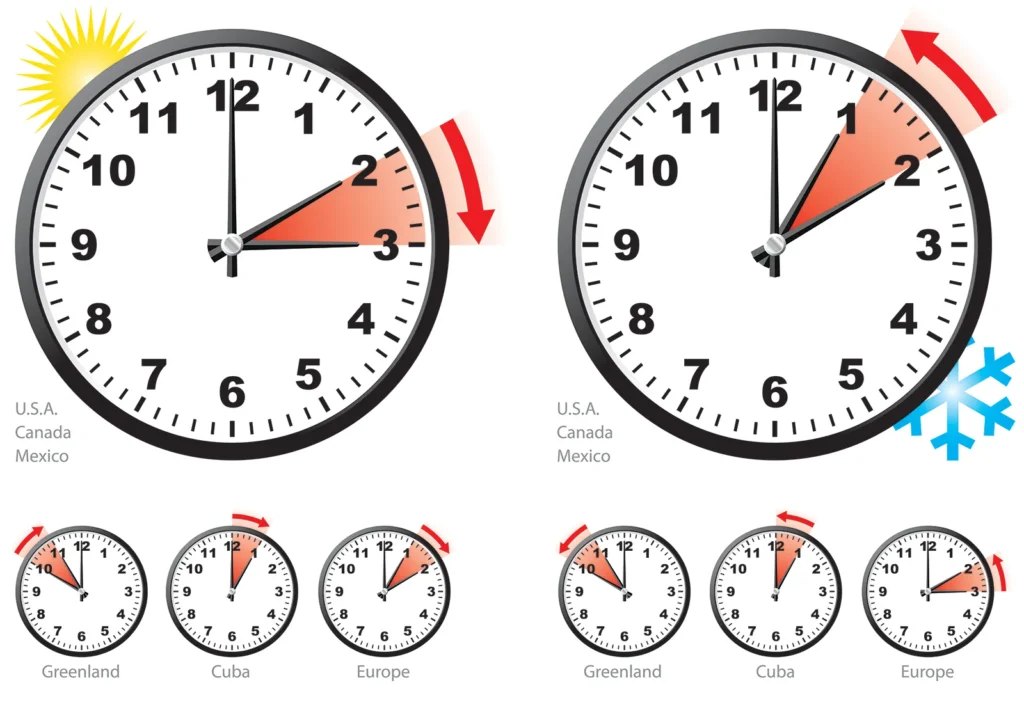
Daylight Saving Time 2025: Key Dates and the Early Endpoint
In 2025, Daylight Saving Time in the United States begins on Sunday, March 9, at 2:00 AM, when clocks spring forward one hour. This marks the start of longer evenings, ideal for outdoor activities and extended productivity.
The much-discussed DST endpoint – the “fall back” – occurs on Sunday, November 2, 2025, at 2:00 AM, where clocks are set back one hour. This date is slightly earlier than in 2024 (November 3), due to the calendar alignment with the first Sunday in November rule. This early endpoint means an extra hour of sleep sooner, but it also signals the onset of shorter days and potential seasonal affective disorder (SAD) for some.
Why is this endpoint considered “early”? In the context of recent years, November 2 is the second-earliest possible date, prompting conversations about its effects on daily life. For those in regions observing DST, this change affects everything from flight schedules to stock market openings.
Exceptions exist: Hawaii, most of Arizona (except the Navajo Nation), and U.S. territories like Puerto Rico do not observe DST, maintaining standard time year-round.
Globally, DST 2025 follows similar patterns. In Europe, it starts on March 30 and ends on October 26. Countries like Canada align closely with the U.S., while Australia observes it from October to April in relevant states.
To stay updated on time changes, refer to external resources like TimeandDate.com.

The Health Impacts of Daylight Saving Time Changes in 2025
The time shifts associated with DST aren’t just about resetting clocks; they can significantly affect health. The spring forward in March 2025 may lead to sleep disruption, increasing the risk of heart attacks by up to 24% the following Monday. Studies link this to circadian rhythm disturbances, exacerbating conditions like depression, anxiety, and seasonal affective disorder.
The fall back in November 2025, while granting an extra hour, isn’t without issues. It can slow metabolism, lead to weight gain, and trigger cluster headaches due to altered light exposure. Research from Johns Hopkins indicates acute rises in strokes and heart attacks post-change.
Long-term, repeated DST transitions may contribute to chronic sleep deprivation, impacting cognitive function and immune response. A 2020 study highlighted increased cardiovascular morbidity after the spring shift.
For tips on mitigating these effects, see our Sleep Optimization Guide.
External link: Learn more from the American Heart Association.
Economic Implications of DST 2025: Costs vs. Benefits
Economically, DST 2025 presents a mixed bag. Proponents claim it saves energy and boosts retail spending by encouraging evening activities, with estimates of $1.2 billion in annual savings from reduced traffic accidents alone. The stock market may see gains, with the S&P 500 averaging 7.5% higher during DST periods.
However, critics point to hidden costs. The time changes can lead to productivity losses, with one estimate pegging the U.S. economic toll at over $434 million annually from sleep deprivation and errors. Health-related expenses, including $374 million from increased heart attacks and $251 million from strokes, add up to around $670 million in metropolitan areas.
Globally, ending DST could yield welfare gains equivalent to 754 euros per capita per year in Europe. Industries like agriculture oppose DST due to disrupted schedules, while tourism benefits.
For business owners, explore our Productivity Tools Review.
External resource: Wikipedia on DST Analysis.
Global Perspectives on Daylight Saving Time in 2025
DST isn’t uniform worldwide. In 2025, over 70 countries observe it, including most of Europe, North America, and parts of Asia and Africa. For example, Iran starts DST on March 21, Cuba on March 9, and Kazakhstan has observed it since 1981.
In the Southern Hemisphere, like Australia, DST runs from October to April. Some nations, such as Japan and India, never adopted it, while others like Turkey maintain permanent DST.
Controversies abound: The EU has debated scrapping DST since 2018, with no resolution by 2025. In the U.S., proposals for permanent DST, like the Sunshine Protection Act, stalled in Congress.
For international travel tips, check Global Time Zone Navigator.
Tips for Adjusting to the DST Endpoint in 2025
Preparing for the November 2, 2025, time change can minimize disruptions. Start by gradually shifting your sleep schedule a week in advance. Use the extra hour for relaxation or exercise to combat potential mood dips.
Update devices manually if needed, and review schedules for appointments. For health, maintain consistent meal times and exposure to natural light.
Parents: Help kids adjust with earlier bedtimes. Businesses: Communicate changes to employees.
See our Seasonal Adjustment Hacks.
The Future of Daylight Saving Time Beyond 2025
Momentum is building to end clock changes. Polls show 54% of Americans favor permanent standard time. States like Florida and California have passed laws for permanent DST, awaiting federal approval.
Globally, countries like Russia and Belarus have opted for permanent time, citing health benefits. If changes occur, 2025 could be one of the last years with traditional DST.
Embrace the Time Travel in 2025
As we approach the early DST endpoint on November 2, 2025, remember that this “time travel” is more than a clock adjustment – it’s an opportunity to reflect on how time affects our lives. By understanding daylight saving time 2025, you can better prepare for its impacts on health, economy, and daily routines.
Stay tuned to Likiy.net for more updates. Share your DST experiences in the comments, and explore Related Articles.
Frequently Asked Questions About Daylight Saving Time 2025
1. When does Daylight Saving Time start and end in 2025?
In the United States, Daylight Saving Time 2025 begins on Sunday, March 9, at 2:00 AM, when clocks “spring forward” one hour. It ends on Sunday, November 2, at 2:00 AM, when clocks “fall back” one hour. This early endpoint in November is notable as it aligns with the first Sunday of the month. For more on time management during seasonal changes, visit our Time Management Strategies.
2. Why is the DST endpoint in 2025 considered early?
The DST end 2025 on November 2 is earlier than some previous years, like 2024’s November 3, due to the calendar’s alignment with the first Sunday in November rule. This shift means shorter evenings arrive sooner, impacting schedules and activities. Learn how to adjust with our Seasonal Adjustment Hacks.
3. Which regions do not observe Daylight Saving Time in 2025?
In the U.S., Hawaii, most of Arizona (except the Navajo Nation), and territories like Puerto Rico, Guam, and the U.S. Virgin Islands do not observe DST, sticking to standard time year-round. Globally, countries like Japan, India, and China also skip DST. For international time zone tips, check our Global Time Zone Navigator.
4. How does the DST time change affect health?
The time change fall 2025 can disrupt sleep and circadian rhythms, potentially increasing risks of heart attacks (up to 24% post-spring forward), strokes, and mood disorders like seasonal affective disorder (SAD). The fall back may cause slower metabolism or cluster headaches. Mitigate these effects with tips from our Sleep Optimization Guide or the American Heart Association.
5. What are the economic impacts of DST in 2025?
DST can boost retail and tourism by extending evening daylight, with estimated savings of $1.2 billion from reduced traffic accidents. However, productivity losses and health-related costs (e.g., $670 million from heart attacks and strokes) pose challenges. For business owners, explore our Productivity Tools Review. Learn more at Wikipedia’s DST Analysis.




